What are security ratings?
UpGuard calculates a security rating through quantitative assessment of your external cybersecurity posture.
UpGuard’s proprietary scanning infrastructure monitors and collects billions of data points daily through trusted commercial, open-source, and proprietary methods. Our focus is on non-invasive, passive data collection, which can be uniquely performed at scale and on-demand.
To produce an organization's security rating, UpGuard calculates a weighted average of the automated scan data for owned assets and combines that with the organization's questionnaire score (if applicable). Automated scanning contribute 50% of the overall security rating, with the questionnaire score contributing the remaining 50%.
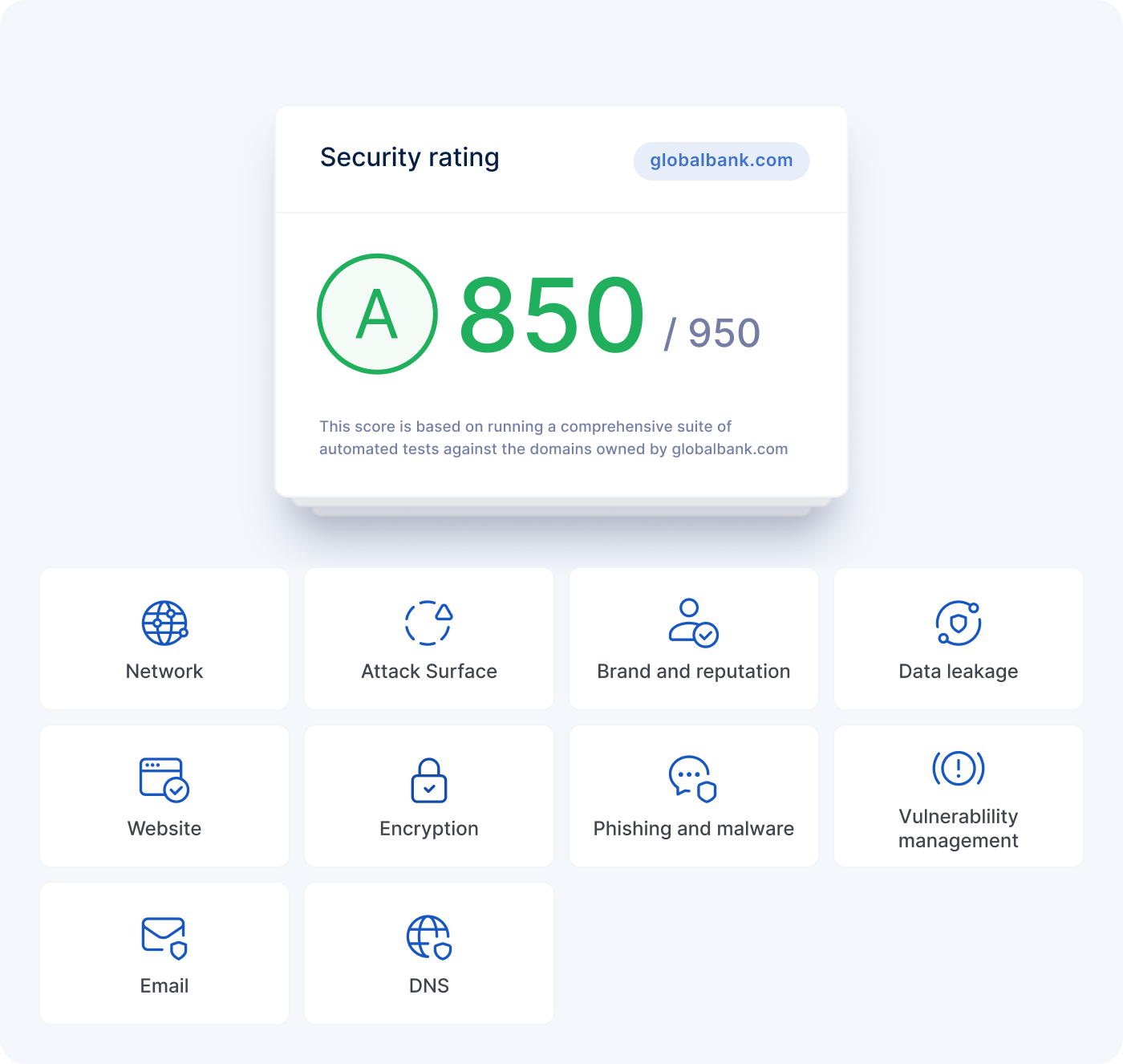
Each category is given a weighting based on the total number of risks in the category and the severity of the category's risks. If you have many open risks with high severities in a category, that category will receive more weight toward your organization's security rating.
UpGuard analyzes and calculates a security rating out of 950 using a proprietary, subtractive scoring algorithm. Assets begin with a complete score of 950 and then decrease as they fail cybersecurity review for specific threat signals. Deductions are weighted by the severity of the risk (critical, high, medium, low). While the security rating can be indicative of your external security posture, it's also important to assess how your score is affected.
You receive both a numeric score out of 950 and a corresponding letter grade:
-
A — 801-950: Organization has a robust security posture and good attack surface management.
-
B — 601-800: Organization has reasonable security controls in place but could have gaps in their security posture.
-
C — 401-600: Organization has poor security controls and has serious issues that need to be addressed.
-
D — 201-400: Organization has severe security issues that need to be addressed and should not process any sensitive data.
-
F — 0-200: Organization has not invested in basic security controls.
See also:
